Spine
The vertebral column, also called the backbone, extends from the skull to the pelvis. It accounts for two-fifths of total body weight and is made up of connective tissue and a series of bones, called vertebrae, which are superimposed in the form of a column, hence the term spinal column. The vertebral column is made up of 24 vertebrae + sacrum + coccyx and forms, along with the head, sternum and ribs, the axial skeleton.
| VERTEBRAL COLUMN - OVERVIEW |
 |
| Source: NETTER, Frank H.. Atlas of Human Anatomy. 2nd edition Porto Alegre: Artmed, 2000. |
Superiorly, it articulates with the occipital bone (skull); inferiorly, it articulates with the hip bone (iliac).
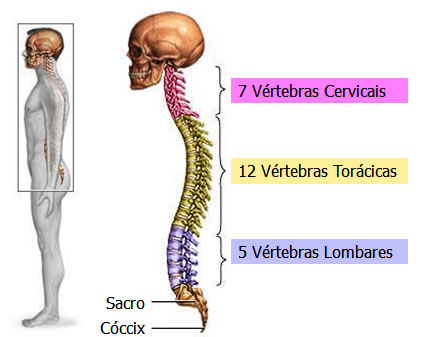
The spine is divided into four regions: Cervical , Thoracic , Lumbar and Sacro-Coccygeal .
There are 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral and about 4 coccygeal vertebrae .
| VERTEBRAL COLUMN - REGIONS AND VERTEBRAE |
 |
| Source: ADAM . |
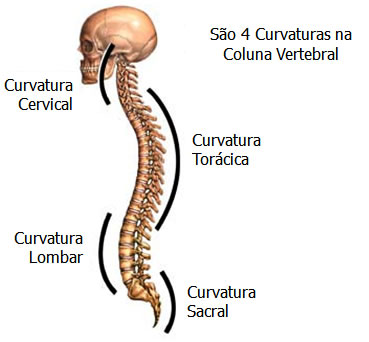
Curvatures of the Vertebral Column
In a side view, the spine presents several curvatures considered physiological.
Are they:
- Cervical (ventrally convex – LORDOSE),
- Thoracic (ventrally concave – CYFOSIS),
- Lumbar (ventrally convex – LORDOSE)
- Pelvic (ventrally concave – CYFOSIS).
When one of these curvatures is increased, we call it HYPERCYPHOSIS (dorsal and pelvic region) or HYPERLORDOSIS (cervical and lumbar region).
In an anterior or posterior view, the spine does not show any curvature. When any curvature occurs in this plane we call it SCOLIOSIS .
| VERTEBRAL COLUMN - CURVATURES |
 |
| Source: ADAM . |
Spine Functions
- Protects the spinal cord and spinal nerves;
- Supports body weight;
- Provides a partially rigid and flexible shaft for the body and a pivot for the head;
- It plays an important role in posture and locomotion;
- Serves as an attachment point for the ribs, pelvic girdle and back muscles;
- It provides flexibility for the body, being able to flex forward, backward and sideways and even rotate about its major axis.
Vertebral Canal
 The spinal canal follows the different curves of the spine. It is large and triangular in regions where the spine has greater mobility (cervical and lumbar) and is small and round in the region that does not have much mobility (thoracic).
The spinal canal follows the different curves of the spine. It is large and triangular in regions where the spine has greater mobility (cervical and lumbar) and is small and round in the region that does not have much mobility (thoracic).
In the image to the side (top view of the spine), we can see the spinal canal. It is formed by the junction of the vertebrae and serves to protect the spinal cord. In addition to the spinal canal, the spinal cord is also protected by the meninges, the cerebrospinal fluid and the blood-brain barrier.
The vertebrae can be studied under three aspects: general, regional and individual characteristics.
| General features | Regional Features | Individual Characteristics |
In the vertebral column we also find the sacrum (about four or five fused vertebrae – non-mobile) and inferior to it, the coccyx (fusion of 4 vertebrae – non-mobile) is located.
| Sacrum | Coccyx |
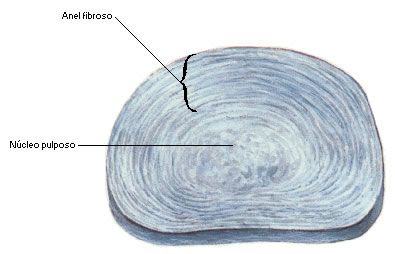
Intervertebral Disc
Between the bodies of two adjacent vertebrae from the second cervical vertebra to the sacrum, there are intervertebral discs.
Consisting of a peripheral fibrous disc composed of fibrocartilaginous tissue, called FIBROUS RING ; and an internal, elastic, soft substance called the NUCLEUS PULPOSUS . The discs form strong joints, allow various spinal movements and absorb impacts.